Kalshi Forecasts Beat Traditional Models in New Federal Reserve Study

A newly released Federal Reserve paper dated February 19, 2026, is drawing attention to the growing role of prediction markets in macroeconomic analysis.
- Kalshi correctly predicted every FOMC rate decision from 2022 to 2025 (measured one day before meetings).
- Its forecasts outperformed Fed funds futures and beat Bloomberg on headline CPI.
- For core CPI and unemployment, accuracy matched traditional forecasts.
- Traders see a 92% chance of a March rate hold, with high odds of a hawkish dissent.
Titled “Kalshi and the Rise of Macro Markets,” the study by Anthony Diercks, Jared Katz, and Jonathan Wright examines how the event-based trading platform Kalshi performs relative to traditional forecasting tools.
The findings suggest that prediction markets are not just speculative arenas but increasingly reliable sources of real-time economic expectations – in some cases outperforming long-established benchmarks.
Perfect Record on FOMC Decisions
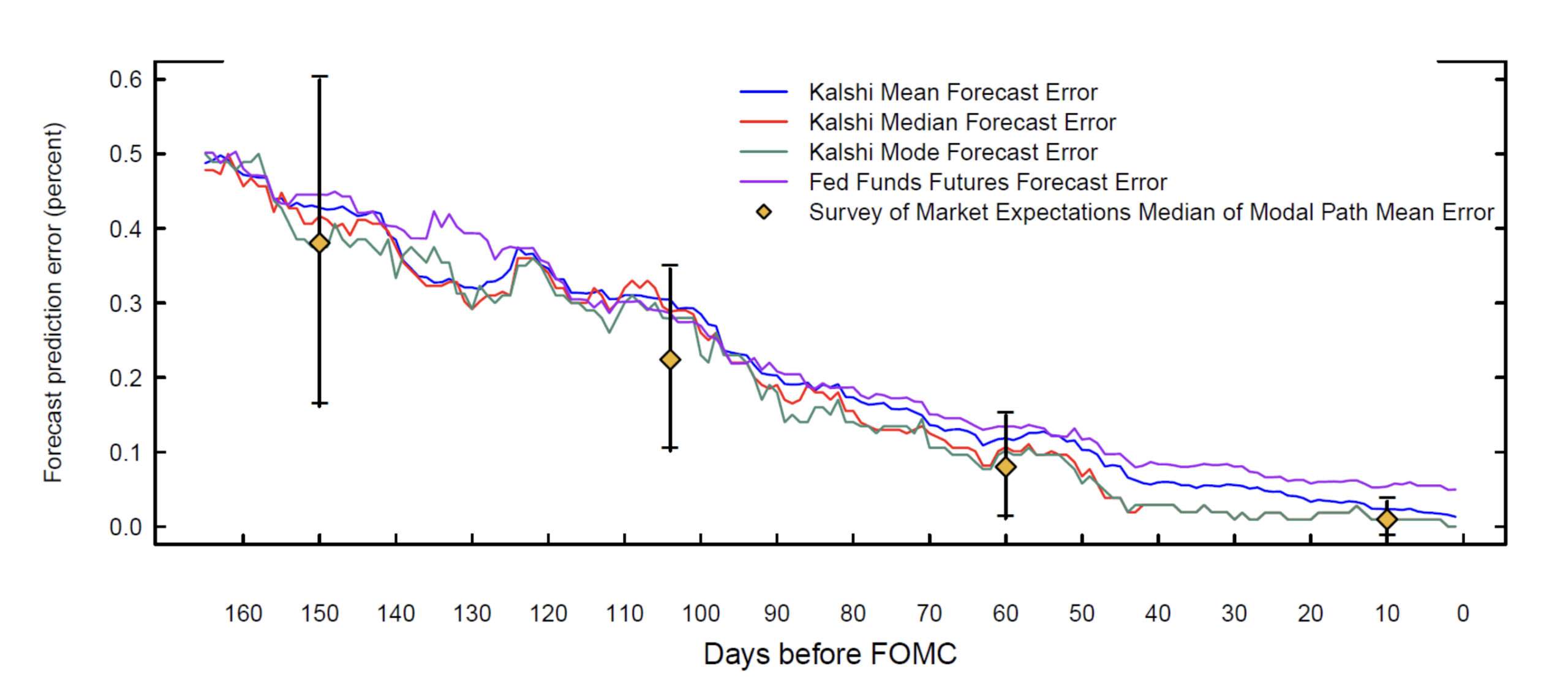
The researchers found that Kalshi maintained a flawless record when forecasting Federal Open Market Committee decisions between 2022 and late 2025, based on probabilities measured the day before each meeting. This included accurate median and modal forecasts across every decision in that period.
Notably, Kalshi’s projections showed a statistically significant improvement over Fed funds futures contracts when predicting rate outcomes. In inflation forecasting, the platform also delivered a measurable edge over the Bloomberg consensus for headline CPI readings.
For core CPI and unemployment data, however, Kalshi’s forecasts were statistically similar to Bloomberg’s consensus, with nearly identical error margins.
Why Prediction Markets Stand Out
The paper outlines several structural advantages that distinguish prediction markets from traditional survey-based or derivatives-based indicators.
First, Kalshi provides continuously updating intraday pricing. In contrast, the New York Fed’s Survey of Primary Dealers offers a snapshot only once every six weeks. This high-frequency data allows policymakers and investors to monitor shifting expectations in real time.
Second, Kalshi fills what the authors describe as “market holes.” For variables like GDP, core inflation, and unemployment – where options markets are often thin or nonexistent – Kalshi contracts provide distributional forecasts that capture uncertainty and skewness.
Third, unlike Fed funds futures, which average expectations over an entire month, Kalshi contracts are tied to specific FOMC meeting dates. This design allows for a cleaner probability distribution around a single decision rather than a blended monthly rate.
Real-Time Reaction to Policy Signals
The study also tracked how Kalshi markets respond to new information. Implied rate probabilities adjusted quickly following official communication from Federal Reserve officials.
For example, the probability of a July rate cut rose to 25 percent after remarks from Governor Christopher Waller and Governor Michelle Bowman. However, that probability declined sharply after the release of a stronger-than-expected June payrolls report.
The researchers observed that uncertainty around rate expectations typically declines after major data releases – particularly inflation prints – as the distribution of market-implied outcomes tightens.
READ MORE:

Bitcoin vs Gold 2025-2026 Outlook: Can BTC Reclaim Dominance After Gold’s Historic Rally?
Biases and Caveats
Despite the strong performance metrics, the paper identifies certain structural biases.
One recurring pattern is the so-called “favorite-longshot bias.” Contracts priced below $0.10 tend to win less frequently than implied, while contracts priced above $0.50 often generate positive returns beyond expectation. This suggests some systematic mispricing at the extremes.
The authors also stress that the paper is preliminary and meant to stimulate discussion. It does not represent an official policy endorsement from the Federal Reserve System.
March FOMC Outlook
Current Kalshi pricing shows traders assigning a 92 percent probability that the Federal Open Market Committee will maintain the target federal funds rate at 3.50 percent to 3.75 percent at the March 18, 2026 meeting.
There is also an 88 percent probability of what traders describe as a “hawkish hold,” implying at least one dissenting vote. Stephen Miran is viewed as the most likely dissenter, with a 92 percent implied probability, followed by Christopher Waller at 61 percent.
The study’s broader takeaway is clear: prediction markets like Kalshi are becoming increasingly relevant in shaping expectations around monetary policy, offering a dynamic complement to traditional surveys and futures-based indicators.
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice. Coindoo.com does not endorse or recommend any specific investment strategy or cryptocurrency. Always conduct your own research and consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions.