Technology is evolving, and this makes many things change around it. While the technology updates are truly surprising and challenge all of us to adapt to new platforms and new ways to use various things, it is truly stunning how much the online space has changed since the emergence of crypto.
Now, crypto might sound a little confusing. How have some digital coins changed the internet, right? However, it is not crypto coins and tokens that changed it, but the technology behind them.
Cryptocurrencies differ greatly, but they will always have some things in common: blockchain technology and, basically, decentralization. And such concepts can and are applied in many other industries, including retail, healthcare, and politics. So, it was also impossible for them not to enter the Internet circle.
In this article, we will discuss how the internet has changed over time and the one “battle” that triggers plenty of us: Web3 vs. Web2.
How It Started – Web1
The internet started small, just like many other things. First, there was Web1. The technology was developed by Tim Berners-Lee, whose main idea was to build a decentralized protocol to allow users to share data from anywhere they might be.
Although it was the first version of the World Wide Web and was not so advanced, Web1 had one main limitation: it was mostly controlled by some specific companies, and users could only read the content they published. This is why we think of Web1 as a “read-only” version.
How It’s Going – About Web2
Once social media platforms were developed, the internet started to become more “read-write” rather than “read-only.” Users were able to publish their content on the internet. And this was possible by having just mobile internet access or connection. Starting with 2004, not only companies were providing content, but users were also offered platforms where they could share user-generated content and interact with one another.
This version of the World Wide Web is called Web2, and we still use it these days. It mainly focuses on static websites, social media platforms, e-commerce, and search engines. Through various advanced web browser technologies, Web2 makes everything clickable and allows users to interact, thus bringing many significant advantages to the table when compared to Web1. The loading time of elements such as images is also reduced thanks to a concept called content delivery network.
Benefits and Limitations of Web2
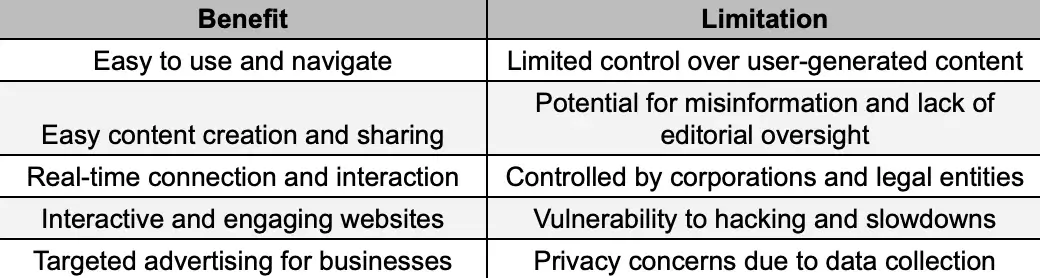
Benefits of Web2
- Easy to use – There is no internet user who does not know how to search for specific information on a search engine. We all got used to it, and we know how to use it to our advantage;
- Share information – With so many social media platforms, we are able to share our thoughts and knowledge as easily as possible. All a user has to do is write their content, log into the platform, and post it. This allows us to share or look for user-generated content using various platforms;
- Communicate – There is nothing better than being able to communicate online with that friend who left the country to work in Australia, right? Well, Web2 does that for you. By simply accessing a social media platform such as Facebook or Instagram, you can write a message or send something that will be delivered in seconds, if not less. This allows for user interaction, and this is truly valuable. Furthermore, users can build their own websites with the help of various tools, such as free web hosting services;
- Access dynamic content – Web1 was pretty dry when it comes to design and usability. However, Web2 provides websites where you can click on almost anything. These days, websites have buttons and links that allow us to take action with a click;
- Advertise – When on Web1, advertising was not allowed. It would have been pretty hard to build specific ads, as the web pages were static and supported simple digital images and a limited number of hyperlinks. But on Web2, you are now able to advertise your business easily.
Limitations of Web2
- It is still controlled by major organizations – There are many entities that actually control the internet and censor data found online. Corporations and legal authorities are some of the biggest, and they can control or even block specific information to shape the internet to their advantage. We should not always think of them badly, but there are situations in which this might happen. Of course, it’s for the best not to be able to post harmful content on a social media platform or to promote specific products or services to a wide audience, as this can affect many users. But such practices still raise the question of expression. Web2 is read-write, but are we actually able to write as we might like? Are we controlled to some extent?
- Security is low – We all know that Web2 is safe, but not enough. The current version of the WWW relies on centralized servers, which can affect many worldwide users. If a hacker wants to gather some information, they need to breach a single system to gain access to it.
- Data is owned by others – Don’t take it wrong, but giant companies collect and can always access data. It should not be surprising, as you are at least informed whenever you create an account, or you sign in with your email to various platforms. Cookies also help companies collect data about you and your behavior on a website. Such data reaches website owners’ servers, and it stays there for as long as they want. This can be a significant privacy issue.
How It’s Gonna Be – Web3, Briefly
Also called “the semantic web,” Web3 revolutionizes how we use and perceive the internet. There are plenty of differences between Web2 and Web3, and some of them can be significant advantages.
The idea of Web3 was first mentioned by Gavin Wood, one of Ethereum’s co-founders. The main goal of Web3 is to reduce or even eliminate the trust we now have in major companies that control the online space. Decentralization is the concept that helps developers build what we will call “the decentralized web.”
Web3 goes beyond social media platforms and the ability to express yourself online. While Web1 was read-only and Web2 was read-write, Web3 will be read-write-own. Thus, the 3rd generation of the WWW offers internet users the power of ownership. Concepts such as decentralized data networks, NFTs, artificial intelligence, machine learning, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies can be used to allow users to own data.
Benefits and Limitations of Web3
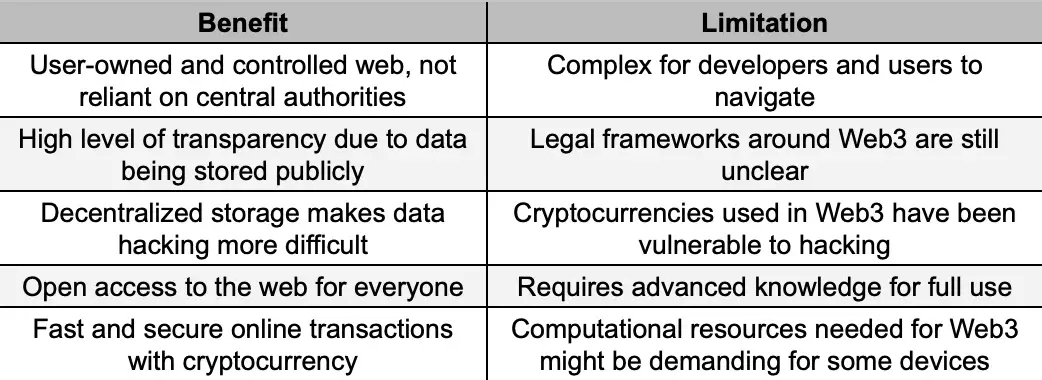
Benefits of Web3
Decentralized
The main feature of Web3 and the major difference between Web3 and Web2 surely is the fact that it is decentralized. Developers can store data on a computer network spread worldwide by basing each platform on a decentralized network. Furthermore, instead of being controlled by a specific central authority, Web3 is owned by all web users. The ownership is basically distributed among all the developers and users.
Transparent
Decentralization is a concept that comes with numerous benefits. One of them is the high level of transparency the semantic web provides. Considering that there is no need for third parties anymore and everything is stored online, it will be significantly easier to access any data on the internet. Everything will be extremely transparent.
It’s just like with cryptocurrencies. Unlike fiat, you can see the details of crypto transactions once you enter a network. This means that transactions are transparent and can be accessed by any crypto user.
Secure
Decentralization makes everything extremely secure. We mentioned before that in Web2’s case, data is stored on central servers and can be easily accessed by hackers. On Web3, however, data is stored on peer-to-peer networks that would take forever to access, as information is stored in numerous points from all over the world.
Permissionless
Another significant advantage of Web3 is that it is permissionless. This means there is no need for permission to use specific internet features. Everyone has equal access to Web3, allowing users to navigate freely. No one gets excluded, and users have complete control over their data and content.
Uses Crypto
Web3 uses cryptocurrencies to complete transactions online, no matter their type. Since crypto is decentralized, fast, and secure, the whole online space also has these qualities. Users can send or receive crypto in seconds without the need for third parties or other central authorities.
Limitations of Web3
Complexity
Compared to Web2, Web3 is extremely complex. And we’re not only talking about the development side. Users will find it hard to use Web3, too, as it implies various complex concepts, such as smart contracts, decentralized apps, and many more. This is why mass adoption might be a little hard to achieve. In general, Web3 requires advanced programming knowledge, so newcomers should put some effort into using it.
Legal Issues
We all know that crypto is unregulated. Web3 is based on blockchain and is entirely different from what we are used to now. Thus, the main challenge would be to enforce legal frameworks on blockchain technology, just like central authorities find it hard to do so for crypto. The lack of regulations might lead to some illegal activities on Web3, such as fraud or money laundering.
Security Concerns
Web3 will use crypto to complete online transactions, but crypto itself can be and has been subject to some major hacks over time. Hackers will always find a way to get where they don’t truly belong, and users are still concerned whether their crypto funds are safe on the internet.
Computational Resources
Web3 uses advanced technologies to function as planned, and some of the devices we use these days might not be suitable for working with Web3. Thus, users might also have to ensure that they have advanced devices and more computational power to use Web3. This can also affect the transition from Web2 to the semantic web.
Scalability Issues
We all know the 3 features that all cryptocurrencies aim to reach. The concept is called “The Blockchain Trilemma” and says that no network can achieve decentralization, security, and scalability all at the same time. And this might be the problem with Web3, too. Blockchain technology cannot handle large amounts of data well. This can result in slowdowns and affect the overall performance of the Web3 space.
Is Web3 the Future of Online Space?
Considering the major interest in the semantic web and the improvements done with each day that passes, it seems that Web3 might be the future of the internet. Web3 can help us navigate the online space seamlessly, but the transition from Web2 might take longer than anyone expects.
Understanding and using Web3 requires some IT skills, and not all users have it. This might be the biggest downside of the third generation of the internet. However, in time and with some effort, it is possible that we all will be able to use Web3.
Final Thoughts
The internet has changed surprisingly since the 1990s, when Web1 was developed. These days, we have a platform for anything; we can express ourselves online, and we can buy almost anything on a website. Still, things can always be improved, and Web3 comes to do this.
Considering that Web2 is still controlled by internet giants, we are somehow limited when being online. Furthermore, personal information is stored and can be accessed by major companies, and this can worry many online users.
Web3 is entirely decentralized and brings the power of ownership to worldwide users. Along with many other significant benefits, Web3 can become the future of the online space. However, we still need to see how much it will take to switch from Web2 to Web3.


